- Product Details
COVID19 IgG & IgM Antibody Detection Kit (Colloidal Gold Method) For in vitro diagnosis CE MHRA
COVID-19 is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus that spreads easily between people in a similar way to the common cold or ‘flu. Most people with COVID-19 have a mild to moderate respiratory illness, and some may have no symptoms (asymptomatic infection). Others experience severe symptoms and need specialist treatment and intensive care.
The immune system of people who have COVID-19 responds to infection by developing proteins that can attack the virus (antibodies) in their blood. Tests to detect antibodies in peoples' blood might show whether they currently have COVID-19 or have had it previously.
European Directives Compliance:
EN 23640-2015
EN 980:2016
EN ISO 14971:2019
EN 13612:2002
EN 13640:2002
EN 13641:2002
EN ISO 18113-1 2011
EN ISO 18113-4 2011
This kit is suitable for the qualitative detection of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) IgM and IgG antibodies in human whole blood from a finger prick. Common signs of a person infected with a coronavirus include respiratory symptoms, fever, cough, shortness of breath, and dyspnea. In more severe cases, infection can cause pneumonia, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), kidney failure, and even death. Coronavirus can be excreted through respiratory secretions or transmitted through oral fluids, sneezing, physical contact, and through air droplets.
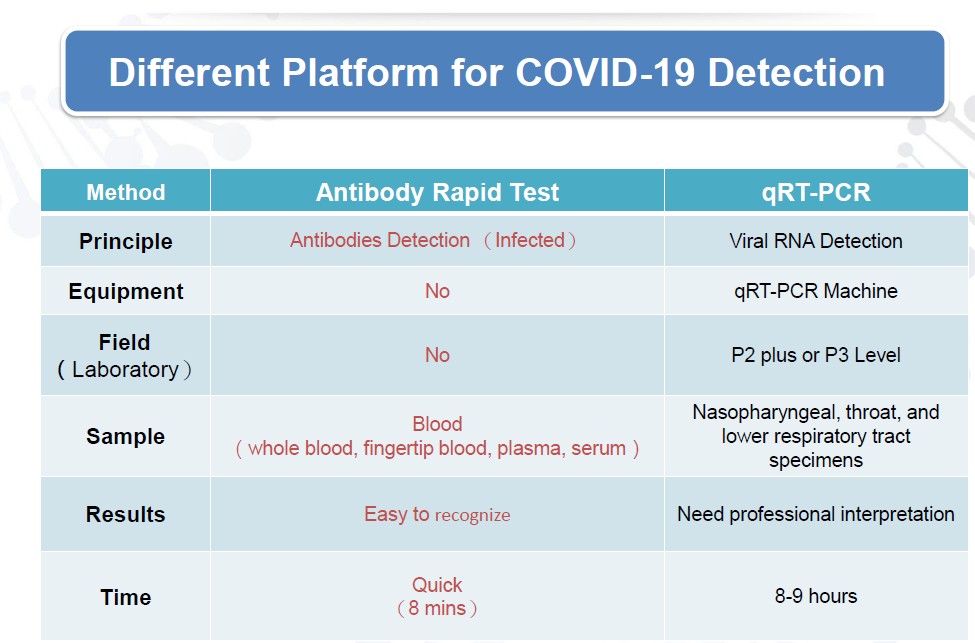
Covid-19 Testkit Detection Platform
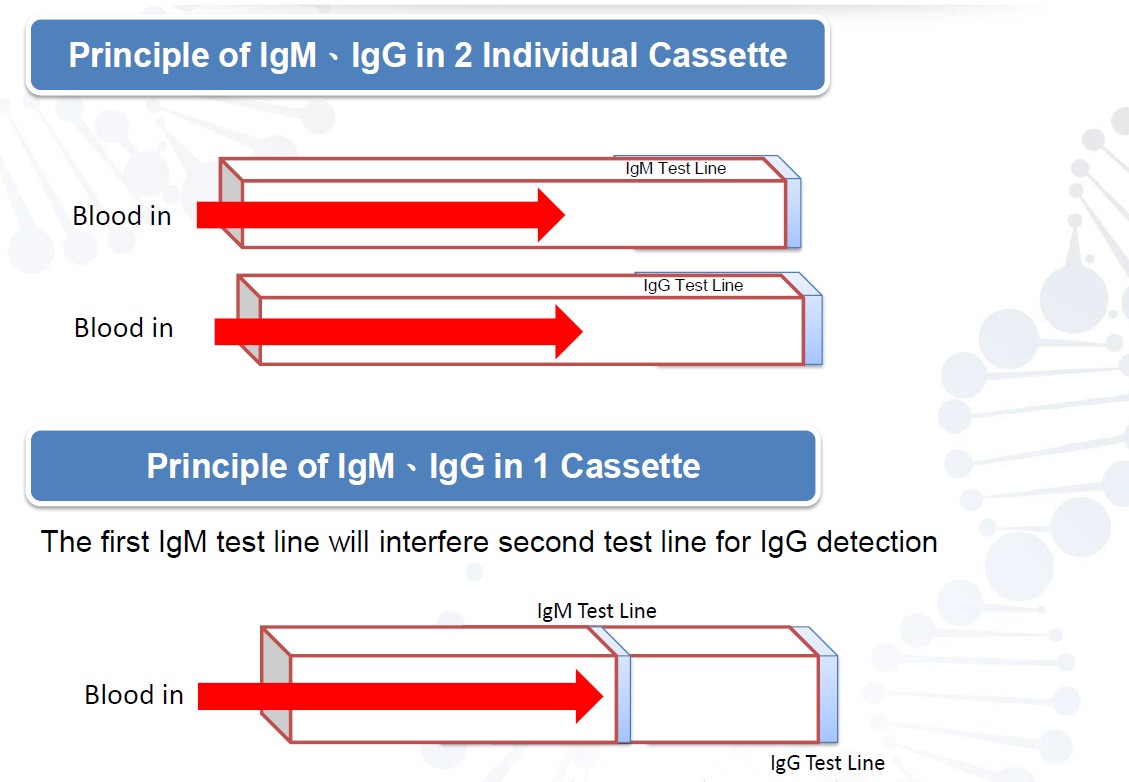
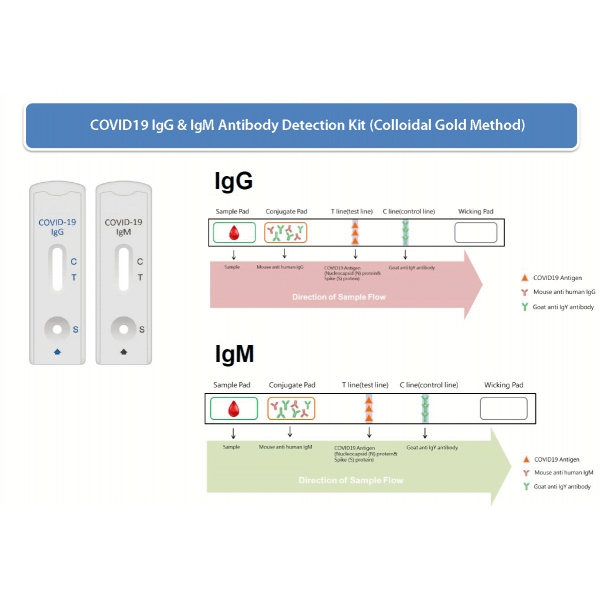
Covid-19 Rapid Test Kit Principal
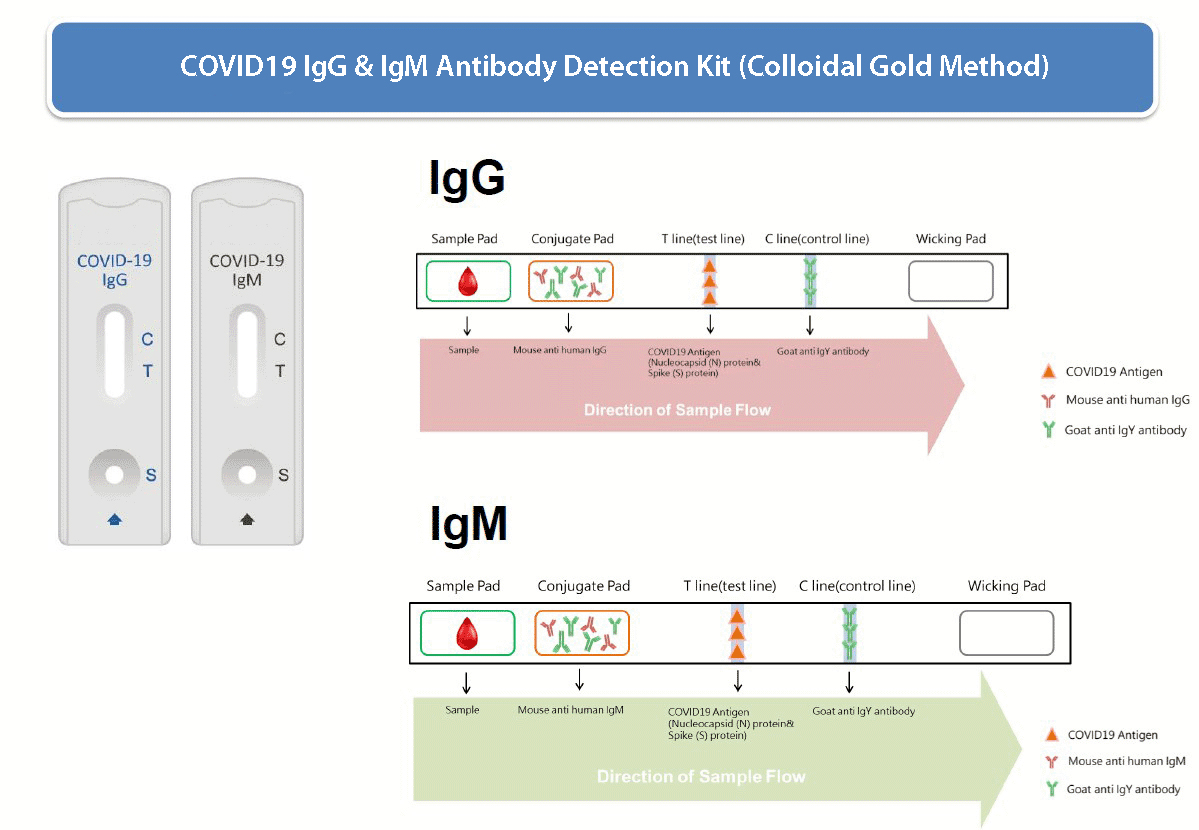
The detection kit uses the principle of immunochromatography: the separation of components in a mixture through a medium using capillary force and the specific and rapid binding of an antibody to its antigen. Each cassette is a dry medium that has been coated separately with novel coronavirus N protein (“T” test line) and anti-mouse antibody (“C” control line) (Figure 2). Free colloidal gold-labeled anti-human IgG are in the release pad section (S). Once diluted serum or whole blood is applied to the release pad section, the anti-human IgM and IgG antibody will bind to coronavirus IgM and IgG antibodies if they are present, forming an IgIgM or Ig-IgG complex. The sample and antibodies will then move across the cassette’s medium via capillary action. If coronavirus IgM or IgG antibodies are present in the sample, the test line (T) will be bound by the Ig-IgM or Ig-IgG complex and develop color. If there is no coronavirus IgM or IgG antibody in the sample, free anti-human IgM or free antihuman IgG will not bind to the test line (T) and no color will develop. The free anti-human antibodies will bind to the control lines (C); these control lines should be visible after the detection step as this confirms that the kit is working properly.
STORAGE AND EXPIRATION Keep kit in a cool and dry place at 2-30°C. Do not freeze the individual kit and / or box. Correctly stored kit are valid for 18 months (see the kit box for expiration information).
SPECIMEN COLLECTION AND PREPARATION a. Sample should be human serum, plasma, fingertip blood and whole blood, other body fluid and samples may cause incorrect or inaccurate results. b. Venous blood should be collected under sterile condition at any time of a day. c. Suggest using serum or plasma for better results. d. Heparin, sodium citrate and EDTA can be used as anticoagulant for plasma, fingertip blood and whole blood sample. e. Sample Volume : 10 μL of serum and plasma sample, 40 μL of fingertip blood and whole blood sample.
INTERPRETATION OF TEST RESULTS a. Positive for COVID-19: The quality control line (C) is colored dark pink, and the test line (T) is colored dark pink or light pink. b. Negative for COVID-19: The test line (T) does not develop color, but the quality control line (C) is colored. c. Invalid: There is no colored control line (C) band. The results are invalid regardless of whether a red band appears on the test line (T); additional testing is required.
What Is an Immunoglobulin Test?
An immunoglobulin (im-yeh-no-GLOB-yeh-len) test measures the level of types of antibodies in the blood. The immune system makes antibodies to protect the body from bacteria, viruses, and allergens.
The body makes different antibodies, or immunoglobulins, to fight different things. For example, the antibody for chickenpox isn't the same as the antibody for covid-19. Sometimes, the body may even mistakenly make antibodies against itself, treating healthy organs and tissues like foreign invaders. This is called an autoimmune disease.
The types of antibodies are:
- Immunoglobulin A (IgA): It's found in the linings of the respiratory tract and digestive system, as well as in saliva (spit), tears, and breast milk.
- Immunoglobulin G (IgG): This is the most common antibody. It's in blood and other body fluids, and protects against bacterial and viral infections. IgG can take time to form after an infection or immunization.
- Immunoglobulin M (IgM): Found mainly in blood and lymph fluid, this is the first antibody the body makes when it fights a new infection.
- Immunoglobulin E (IgE): Normally found in small amounts in the blood. There may be higher amounts when the body overreacts to allergens or is fighting an infection from a parasite.
- Immunoglobulin D (IgD): This is the least understood antibody, with only small amounts in the blood.
Difference Between COVID-19 (Coronavirus) Tests
COVID-19 (Coronavirus) Molecular (Swab) Test
This test uses a long swab to collect material, including physical pieces of coronavirus, from the back of the nose where it meets the throat. A positive result indicates that viral genetic material is present, but it does not indicate that bacterial or other infections also are present. A negative result indicates that the SARS-CoV2 virus that causes the COVID-19 disease was not found. It is possible to have a very low level of the virus in the body with a negative test result.
This test is needed to identify the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes the COVID-19 disease.
COVID-19 (Coronavirus) Antibody (Serology) Test
This is a blood test. It is designed to detect antibodies (immunoglobulins, IgG and IgM) against the coronavirus that causes the disease called COVID-19. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system in response to an infection and are specific to that particular infection. They are found in the liquid part of blood specimens, which is called serum or plasma, depending on the presence of clotting factors. IgM and IgG may either be ordered together or separately.
Having an antibody test is helpful if: your health care provider believes you may have been exposed to the coronavirus which causes COVID19 based on your current or previous signs and symptoms (e.g., fever, cough, difficulty breathing); you live in or have recently traveled to a place where transmission of COVID-19 is known to occur; you have been in close contact with an individual suspected of or confirmed to have COVID-19; oryou have recovered from COVID-19.
Antibody Test for IgG
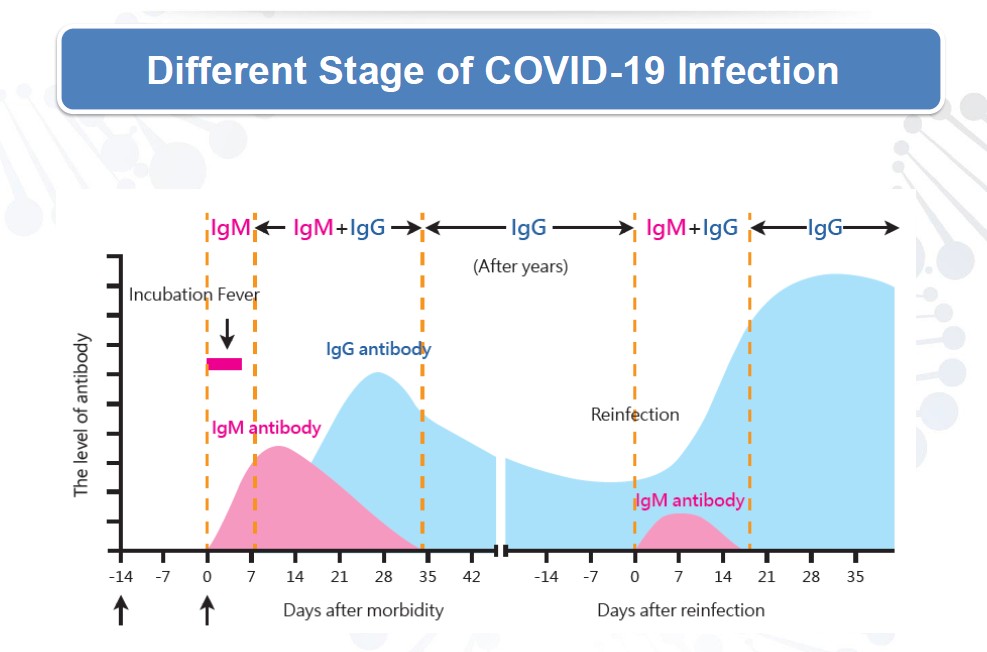
This test detects IgG antibodies that develop in most patients within seven to 10 days after symptoms of COVID-19 begin. IgG antibodies remain in the blood after an infection has passed. These antibodies indicate that you may have had COVID-19 in the recent past and have developed antibodies that may protect you from future infection. It is unknown at this point how much protection antibodies might provide against reinfection.
Antibody Test for IgM
This test detects IgM antibodies. IgM is usually the first antibody produced by the immune system when a virus attacks. A positive IgM test indicates that you may have been infected and that your immune system has started responding to the virus. When IgM is detected you may still be infected, or you may have recently recovered from a COVID-19 infection.
Why are accurate tests important?
Accurate testing allows identification of people who might need treatment, or who need to isolate themselves to prevent the spread of infection. Failure to detect people with COVID-19 when it is present (a false negative result) may delay treatment and risk further spread of infection to others. Incorrect identification of COVID-19 when it is not present (a false positive result) may lead to unnecessary further testing, treatment, and isolation of the person and close contacts. Correct identification of people who have previously had COVID-19 is important in measuring disease spread, assessing the success of public health interventions (like isolation), and potentially in identifying individuals with immunity (should antibodies in the future be shown to indicate immunity).
To identify false negative and false positive results, antibody test results are compared in people known to have COVID-19 and known not to have COVID-19. Study participants are classified as to whether they are known or not known to have COVID-19 based on criteria known as the ‘reference standard’. Many studies use samples taken from the nose and throat to identify people with COVID-19. The samples undergo a test called reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). This testing process can sometimes miss infection (false negative result), but additional tests can identify COVID-19 infection in people with a negative RT-PCR result. These include measuring clinical symptoms, like coughing or high temperature, or ‘imaging’ tests like chest X-rays. People known not to have COVID-19 are sometimes identified from stored blood samples taken before COVID-19 existed, or from patients with respiratory symptoms found to be caused by other diseases.
Documents
COVID19 IgG & IgM Antibody Detection Kit (Colloidal Gold Method) CE Certificate
COVID19 IgG & IgM Antibody Detection Kit (Colloidal Gold Method) MHRA Letter
COVID19 IgG & IgM Antibody Detection Kit (Colloidal Gold Method) English Manual
- Loading...